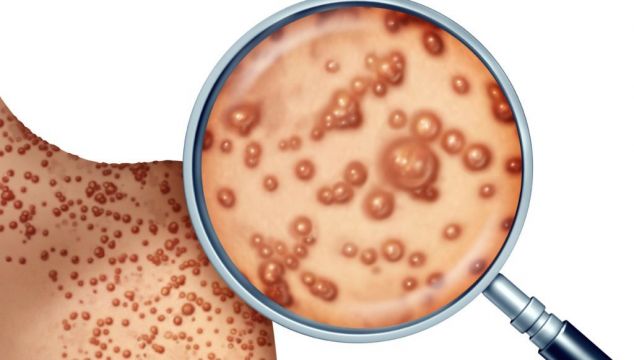
Confirmed monkeypox cases are on the rise in Europe.
A management team has been set up to prepare for the “eventuality” of monkeypox arriving in Ireland, while there are now 57 cases in the UK.
Health officials there say that while the outbreak is “significant and concerning”, the risk to the UK population remains low. The UK government has stocks of the smallpox vaccine, which is being offered to very close contacts of those affected.
Those at the highest risk of contracting the disease are being asked to self-isolate at home for 21 days, with others warned to be on the lookout for symptoms.
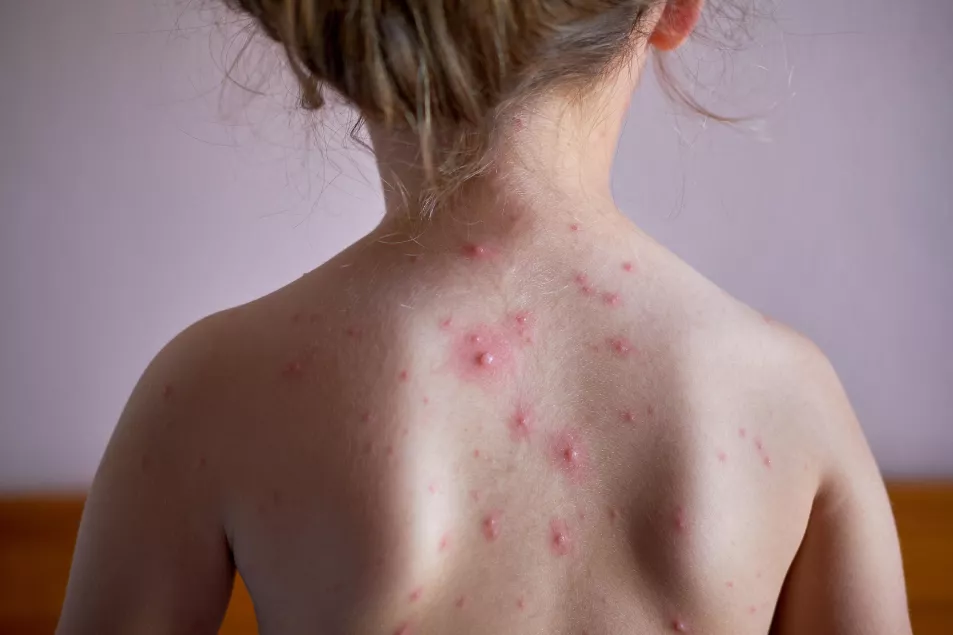
GP and TV personality Dr Nighat Arif says this coincides with a rise in other viruses, saying: “We are seeing an increase in cases of chickenpox, now we are out of lockdown and people don’t want to isolate anymore.”
So, how can you tell the difference between monkeypox and chickenpox in your child?
The symptoms
Arif says the two are “caused by different viruses – monkeypox comes from the smallpox virus, whereas chickenpox comes from the varicella zoster virus”.
She says we haven’t seen monkeypox “in the UK at this level before, and it can spread like chickenpox”.
Monkeypox symptoms include fever, headache, muscle aches, back pain, swollen glands, chills and exhaustion. Within one to five days of the first symptoms, you may notice a rash developing.
The rash will go through several stages. At first, it might look like raised spots, which then might turn into small blisters filled with fluid. They will then form scabs that will later fall off.
We continue to investigate cases of monkeypox in England. Anyone with unusual rashes or lesions on any part of their body, especially their genitalia, should contact NHS 111 or call a sexual health service if they have concerns. Read more: https://t.co/e8jksQo9Av pic.twitter.com/Ncap8Z8aF4
— UK Health Security Agency (@UKHSA) May 22, 2022
Symptoms can last from two to four weeks, and the virus can be spread through skin-to-skin contact.
Chickenpox symptoms include a high temperature, aches and pains, difficulty eating or loss of appetite, and an itchy rash. The rash tends to blister and dry up, creating similar scabs to that of monkeypox.
However, Arif says you should be able to tell the difference between the two. You might find your child’s “temperature will be higher with monkeypox, and they may complain of backache, lower leg aches, chills, and very tender glands around their neck”.
She also shares the “blisters are bigger [with monkeypox]. The chances of them having it are very slim if they haven’t travelled or been in close contact with someone who has”.
The treatment
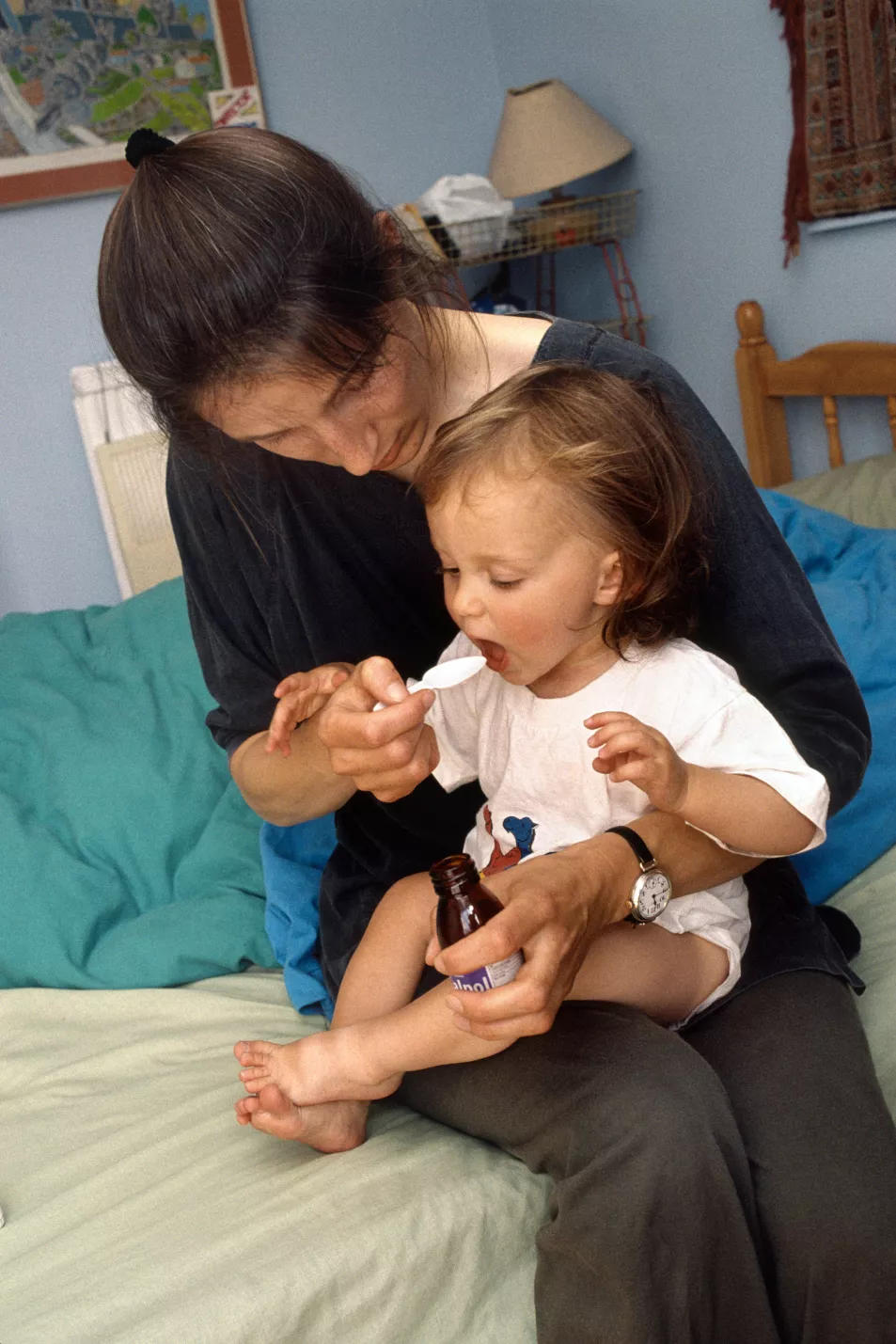

When treating both monkeypox and chickenpox, Arif says: “The incubation period is really important. Isolate until the last blister crusts for chickenpox, but make sure to take three weeks for monkeypox. If your child has chickenpox, please don’t let them into school – isolate them and be careful. It may take a couple of weeks, but it is better than putting people who are vulnerable at risk.”
Arif also suggests using similar treatments to help a child who has chickenpox or monkeypox. “Keep up your intake of fluids, try and eat and give them Calpol to tackle the temperature,” she advises.
If you are struggling to get their temperature down or have any other concerns, speak to a doctor or call 111.
The risks
At present, there is a minimal risk of monkeypox infection, with Arif saying: “We haven’t come across any cases in my surgery. This is not a new virus, and public health [bodies] are very aware of it. Smallpox vaccines are being secured in case there is a problem.”
She suggests the risks are minimal for children with chickenpox or monkeypox. “Monkeypox may make you feel awful when you have it, but [for many people] it is a self-limiting virus and you will feel fine after. However, if you are vulnerable, both can be really dangerous.”
When it comes to chickenpox, “children may get it mildly and then get on with it. But, as with any virus, it is the individuals they come into contact with that may have issues. Adults who haven’t had it, and those who are pregnant or immunosuppressed will have the worst response to the pox.”