Philippine officials have vowed to remove a floating barrier placed by China’s coastguard to prevent Filipino fishing boats from entering a disputed lagoon in the South China Sea.
They said the 980-foot-long barrier at the entrance to the lagoon at Scarborough Shoal is “illegal and illegitimate”.
Chinese coastguard vessels laid the barrier, held up by buoys, on Friday as a Philippine government fisheries vessel approached.
More than 50 Philippine fishing boats were outside the shoal at the time, the Philippine coastguard said.
“We condemn the installation of floating barriers by the Chinese coastguard,” Philippine national security adviser Eduardo Ano said.

“The placement by the People’s Republic of China of a barrier violates the traditional fishing rights of our fishermen.”
Mr Ano said in a statement that the Philippines “will take all appropriate actions to cause the removal of the barriers and to protect the rights of our fishermen in the area”.
He did not elaborate.
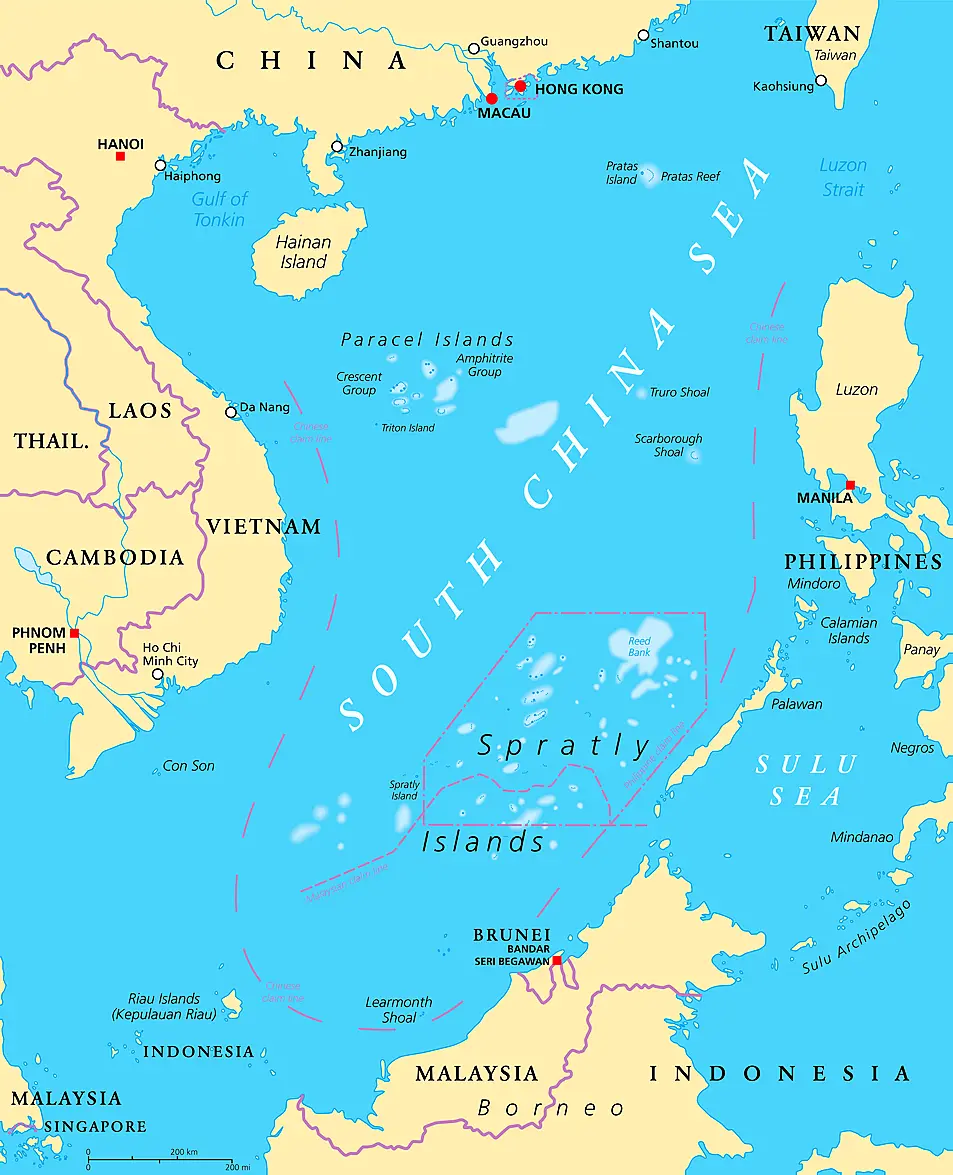
It is the latest flare-up in long-simmering territorial disputes in the busy and resource-rich waterway, most of which is claimed by China.
The Philippines, Vietnam, Malaysia, Brunei and Taiwan are involved with China in the conflicts, which have long been regarded as a potential Asian flashpoint and a delicate fault line in the US-China rivalry in the region.
Washington lays no claim to the sea passageway, a major global trade route, but US navy ships and fighter jets have carried out patrols for decades to challenge China’s expansive claims and promote freedom of navigation and overflight.
China has told the US to stop meddling in what it says is a purely Asian dispute.
The Chinese barrier denies Filipinos access to the rich fishing lagoon surrounded by underwater coral outcrops, Philippine coastguard spokesman Commodore Jay Tarriela said.
He said China’s coastguard installs the removable barrier when Philippine fishing boats show up in large numbers near the shoal.
“It’s an illegal and illegitimate action coming from the People’s Republic of China,” Commodore Tarriela told reporters.
“Definitely it affects our food security.”
A Philippine Bureau of Fisheries and Aquatic Resources ship, which anchored off Scarborough on Friday, and at least 54 Filipino fishing boats were ordered by four Chinese coastguard ships by radio to leave the territory, saying the Filipinos were breaching Chinese and international law.
The Philippine fisheries ship insisted in its radio response that it was on a routine patrol in Philippine waters, Commodore Tarriela said.
The Philippines says Scarborough Shoal lies within its exclusive economic zone, a 200-nautical mile stretch of water where coastal states have exclusive rights to fish and other resources.
Those rights were upheld by a 2016 arbitration decision set up under the 1982 UN Convention on the Law of the Sea, Mr Ano said.
China refused to participate in the arbitration sought by the Philippines in 2013, a year after a tense standoff between Chinese and Philippine ships at Scarborough.
Beijing refused to recognise the 2016 arbitration ruling and continues to defy it.
The 2012 standoff ended with Chinese ships seizing and surrounding the atoll.
Chinese coastguard ships have also blocked Philippine government vessels delivering supplies and personnel to Philippine-occupied Second Thomas Shoal, resulting in near-collisions the Philippine government has condemned and protested.
Washington has said it is obligated to defend the Philippines, its oldest treaty ally in Asia, if Filipino forces, ships and aircraft come under attack, including in the South China Sea.







