Countries are setting out efforts to bring about the end of coal power after 250 years as the Cop26 climate talks focus on pollution from energy.
The move at the crucial conference in Glasgow comes as scientists warn that carbon emissions from fossil fuels look set to rebound to close to pre-pandemic levels in 2021 – and could even rise further in 2022.
Initiatives being announced on Thursday include a UK-led coal-to-clean power transition statement committing countries to ending all investment in new coal power generation domestically and internationally and rapidly scaling up deployment of clean power generation.
The statement also sees them commit to phasing out coal power in the 2030s for major economies and the 2040s for the rest of the world and to ensure the shift away from coal power is fair and benefits workers and communities.
More than 40 countries have signed up to the statement, including 18 committing to phase out and not build or invest in new coal power for the first time, such as Poland, Vietnam and Chile, the UK government said.
Separately, 28 new members have signed up to the “powering past coal alliance”, to phase out the use of the most polluting fossil fuel.
Efforts to swiftly end the use of coal – the single largest contributor to greenhouse gas emissions – are seen as key to cutting carbon enough to get the world on track to limit global warming to 1.5C, beyond which the worst impacts of storms, floods, droughts, wildfires and rising seas will be felt.
Since the Paris climate accord to limit global warming to 1.5C to 2C was agreed in 2015, there has been a 76 per cent cut in the number of new coal plants planned.
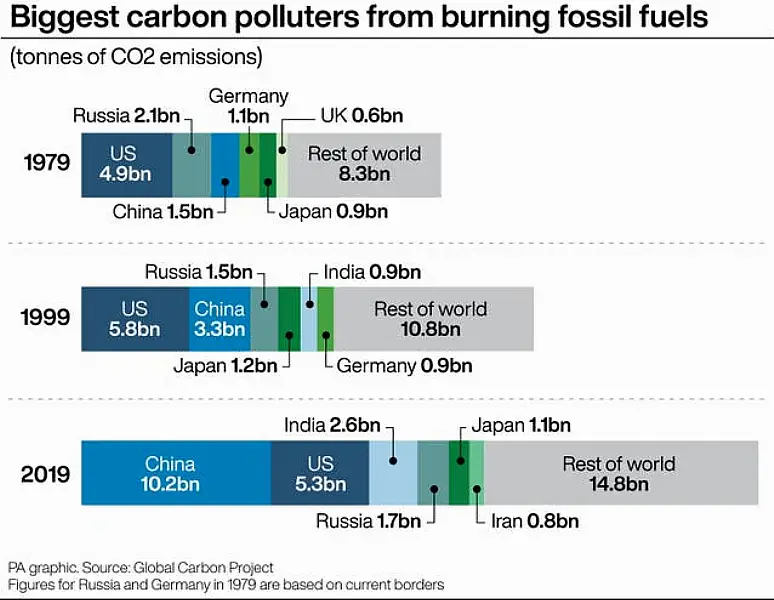
But while it appears the world’s use of coal peaked in around 2014, it is still not falling significantly, with heavy use and even increases in countries such as China.
In May, the International Energy Agency (IEA) warned that investment in new polluting coal power plants and mines, and new oil and gas projects, had to be stopped from 2021 in order to effectively tackle climate change.
In order for the planet to reach net-zero emissions by 2050 – needed to meet the internationally agreed 1.5C goal – global electricity production must hit that target a decade earlier, the IEA said.
Under the latest push, major banks including NatWest have committed to ending finance for coal, in a move coming after commitments from China, Japan and South Korea and the G20 to end overseas finance for coal generation.
Initiatives to phase out coal also include support for emerging economies to move away from the fossil fuel, and to do so in ways that are fair to workers in coal-intensive economies.
UK business and energy secretary Kwasi Kwarteng said: “Today marks a milestone moment in our global efforts to tackle climate change as nations from all corners of the world unite in Glasgow to declare that coal has no part to play in our future power generation.
“Spearheaded by the UK’s Cop26 presidency, today’s ambitious commitments made by our international partners demonstrate that the end of coal is in sight.”
Shadow business secretary Ed Miliband said any progress towards powering past coal is welcome, but there were “glaring gaps” such as a lack of commitment from China and other large emitters to stop increasing coal at home – and nothing on the phasing out of oil and gas.
But Leo Roberts, from climate think tank E3G, said: “The past few days in Glasgow have shown that momentum away from coal is gathering pace, with new partnerships, tools and money coming together to consign coal to history.”
He added that the breadth and depth of announcements and initiatives being announced on Thursday were an indication of how rapidly the shift away from coal is gathering pace, saying: “These announcements collectively demonstrate the era of coal is coming to an end.”
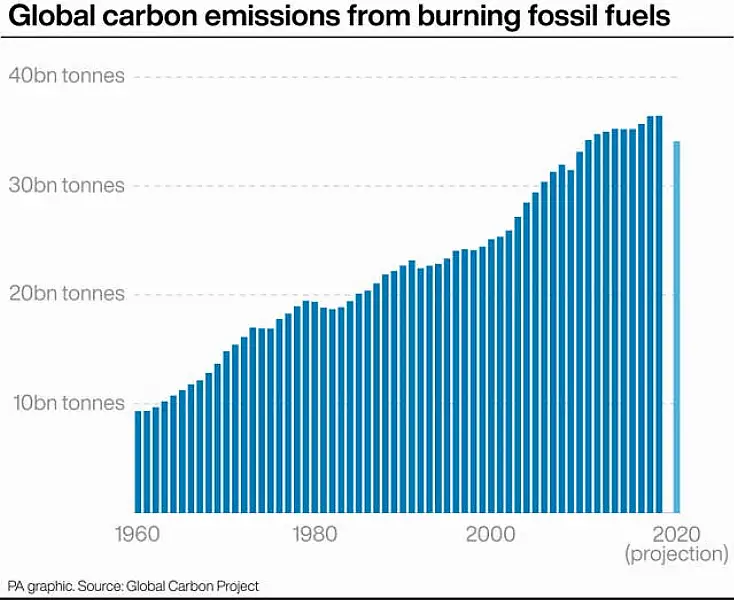
The announcements come as analysis from the Global Carbon Project showed the scale of the challenge, with coal – and gas – emissions set to rise to above 2019 levels in 2021, although oil pollution remains below pre-pandemic levels.
The rapid rise could be a temporary “sugar hit” from stimulus packages that focused on industry, such as in China where emissions continued to rise during 2020, and drove an increased use of coal.
But a further rise in emissions in 2022 to new highs cannot be ruled out if road transport and aviation return to pre-pandemic levels and coal use does not drop back again after the “over-correction” of pandemic stimulus, they said.







