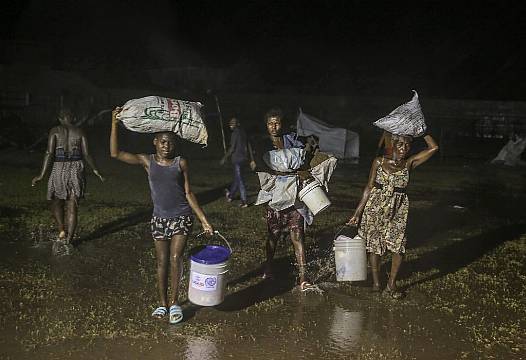Tropical Storm Grace has swept over Haiti with drenching rains just two days after a powerful earthquake battered the impoverished Caribbean nation.
After nightfall, heavy rain and strong winds whipped at the country’s southwestern area, hit hardest by Saturday’s quake, and officials warned that rainfall could reach 15in in some areas before the storm moved on.
Port-au-Prince, the capital, also saw heavy rains.
Grace regained tropical storm status after previously falling to the level of a tropical depression.

The storm arrived on the same day that the country’s Civil Protection Agency raised the death toll from the earthquake to 1,419 and the number of injured to 6,000, many of whom have had to wait for medical help lying outside in wilting heat.
Grace’s rain and wind raised the threat of mudslides and flash flooding as it slowly passed by southwestern Haiti’s Tiburon Peninsula overnight, before heading towards Jamaica and southeastern Cuba on Tuesday.
The quake nearly wrecked some towns in the south west in the latest disaster to befall the Western Hemisphere’s poorest nation.
Haitians were already struggling with the coronavirus pandemic, gang violence, worsening poverty and the July 7 assassination of President Jovenel Moise.
“We are in an exceptional situation,” Prime Minister Ariel Henry told reporters on Monday afternoon as the storm approached.
A hospital in the badly damaged town of Les Cayes was so crowded with patients after the earthquake that many had to lie on patios and in corridors, verandas and hallways, but the approaching storm had officials scrambling to relocate them as best they could.
“We had planned to put up tents (on hospital patios), but we were told that could not be safe,” said Gede Peterson, director of Les Cayes General Hospital.
It is not the first time the hospital has been forced to improvise.

The refrigeration in the hospital’s mortuary has not worked for three months, but after the earthquake struck on Saturday, staff had to store as many as 20 bodies in the small space.
Relatives quickly came to take most to private embalming services or immediate burial.
“We are working now to ensure that the resources we have are going to get to the places that are hardest hit,” said Civil Protection Agency head Jerry Chandler, referring to the hard-hit towns of Les Cayes and Jeremie and the department of Nippes.
Quake victims continued to stream to Les Cayes’ overwhelmed general hospital, waiting on stair steps, in corridors and on an open veranda.
“After two days, they are almost always generally infected,” said Dr Paurus Michelete, who had treated 250 patients and was one of only three doctors on call when the quake hit.
He added that painkillers, analgesics and steel pins to mend fractures were running out amid the crush of patients.
Meanwhile, rescuers and scrap metal scavengers dug into the floors of a collapsed hotel in the coastal town, where 15 bodies had already been extracted.
Jean Moise Fortune, whose brother, the hotel owner and a prominent politician, was killed in the quake, believed there were more people trapped in the rubble.

But based on the size of voids that workers cautiously peered into, perhaps a foot in depth, finding survivors appeared unlikely.
As work, fuel and money ran out, desperate Les Cayes residents searched collapsed houses for scrap metal to sell.
Others waited for money wired from abroad, a mainstay of Haiti’s economy even before the quake.
Anthony Emile waited six hours in a line with dozens of others trying to get money that his brother had wired from Chile, where he has worked since the 2010 quake that devastated Haiti’s capital and killed tens of thousands.
“We have been waiting since morning for it, but there are too many people,” said Mr Emile, a banana farmer who said relatives in the countryside depend on him giving them money to survive.
In Jeremie, police commissioner Paul Menard denied a social media report about looting.
“If it were going to happen, it would have been on the first or second night,” Mr Menard said.
Officials said the magnitude 7.2 earthquake left more than 7,000 homes destroyed and nearly 5,000 damaged from the quake, leaving some 30,000 families homeless.

Hospitals, schools, offices and churches were also destroyed or badly damaged.
Structural engineers from Miyamoto International, a global earthquake and structural engineering firm, visited hard-hit areas to help with damage assessment and urban search and rescue efforts.
Chief among their duties was inspecting government water towers and the damaged offices of charities in the region, said chief executive and president Kit Miyamoto.
Mr Miyamoto said he has seen places devastated by earthquakes build back stronger.
He said the destruction in Port-au-Prince from the 2010 tremor led masons and others to improve their building practices.
People in the capital felt the Saturday morning tremor centred about 75 miles to the west and rushed into the streets in fear but there were not any reports of damage there.
“Port-au-Prince building is much better than it was in 2010 – I know that,” Mr Miyamoto said.
“It’s a huge difference, but that knowledge is not widespread. The focus is definitely on Port-au-Prince.”